Functions depending on the source of vaccines
Of the six core functions introduced on the previous page, all NRAs are responsible for Function 1 (licensing vaccines) and Function 2 (AEFI surveillance). Both these functions should be coordinated with the National Immunization Programme.2, 54
The NRA's can be responsible for Functions 3 – 6 depending on how its respective country obtains vaccines. Countries may:
- Obtain vaccines through United Nations procurement agencies, i.e. United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), WHO, or Pan-American Health Organization (PAHO) Revolving Fund for Vaccine Procurement,
- Procure vaccines directly on the domestic or the international market,
- Manufacture their own vaccines.
The table below shows which responsibilities are taken up by the NRA depending on the source of the vaccine.
NRA functions depending on source of vaccines
| Vaccine-specific NRA functions needed | Areas of activity by NRA (or WHO) depending on source of vaccines | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccine procured by United Nations agency |
Vaccine procured by NRA | Vaccine manufactured in country | |
| FUNCTION 1 Marketing authorization and licensing activities |
 |
 |
 |
| FUNCTION 2 AEFI surveillance |
 |
 |
 |
| FUNCTION 3 NRA lot release |
NRA functions undertaken by WHO on behalf of United Nations agencies or producing countries. |  |
 |
| FUNCTION 4 Laboratory access |
 |
 |
|
| FUNCTION 5 Regulatory inspections |
NRA functions undertaken by producing country. |  |
|
| FUNCTION 6 Oversight of clinical trials |
 |
||
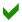
The graphic below shows some of the key capabilities enabling a NRA to implement the 6 core functions listed in the table above.